If you’ve ever adjusted the brightness on your TV, picked a website color in a design tool, or admired the glow of a gaming keyboard, you’ve already worked with RGB—even if you didn’t realize it.
RGB stands for Red, Green, and Blue—the three primary colors of light. By mixing these colors at different brightness levels, screens and LEDs can produce almost every color you see in the digital world. It’s the reason your phone’s display looks vibrant, your photos pop on Instagram, and your favorite streaming shows look true-to-life.
Let’s break it down in plain English—what RGB is, how it works, when to use it, and why it’s different from the colors you see in print.
How RGB Works (And Why It’s All About Light)
The RGB color model uses additive mixing—that means it starts with black and adds light to create color. Each pixel on your screen has three tiny light sources: one red, one green, one blue. By adjusting how bright each one is (from 0 = no light to 255 = full brightness), we can create millions of shades.
Some quick examples:
- RGB(255, 0, 0) → Pure red
- RGB(0, 255, 255) → Cyan
- RGB(255, 255, 255) → White
- RGB(0, 0, 0) → Black
This works because our eyes have light-sensitive cells (cones) tuned to red, green, and blue wavelengths. When those cones get the right mix of light, our brain blends them into a single perceived color

Where You See RGB Every Day
Pretty much any device that emits light and shows color is using RGB:
- Websites & Apps — Every background color, button, and font style is defined in RGB or hex.
- Photography & Video — Cameras capture images in RGB; editing software tweaks those values for the perfect look.
- Digital Displays — TVs, monitors, projectors, and even giant LED billboards all rely on RGB pixels.
- LED Lighting — Smart bulbs, stage lights, and gaming gear use RGB LEDs to create endless color effects.
- Gaming Hardware — Keyboards, mice, and PC cases use RGB lighting for style and personalization.
If it glows and changes color, chances are it’s RGB.

RGB vs. CMYK: Why Screen Colors Don’t Match Print
RGB is perfect for screens, but it doesn’t translate directly to paper. That’s where CMYK—Cyan, Magenta, Yellow, and Key (Black)—comes in.
Here’s the big difference:
- RGB (Additive) → Starts with black and adds light. All colors at full = white.
- CMYK (Subtractive) → Starts with white (paper) and removes light using ink. All colors combined = black (or dark brownish black in practice).
If you design a bright, electric blue in RGB and send it to print without converting to CMYK, it might come out dull or muted. Design software like Photoshop, Illustrator, and Figma let you convert color profiles so you get the closest possible match.

RGB Values, Hex Codes, and Picking the Perfect Shade
Designers and developers often work with two main formats:
- RGB Values → Written like
rgb(255, 99, 71) - Hex Codes → Written like
#FF6347(the same color as above)
You can grab these values using built-in color pickers in tools like Figma, Photoshop, or even your browser’s developer tools. Online RGB color pickers (like RapidTables or rgbcolorpicker.com) are also great for finding shades quickly and seeing how they’ll look on different backgrounds.
RGB in Gaming & Hardware Lighting
RGB lighting has become a design feature in itself—especially in gaming. PC builders and gamers use RGB to light up keyboards, fans, RAM sticks, and entire cases.
With the right software—Corsair iCUE, SignalRGB, Razer Synapse—you can:
- Set a single static color
- Create rainbow wave patterns
- Sync lighting with music, movies, or game events
The principle is exactly the same as your monitor’s RGB pixels—it’s just applied to LEDs instead of a display panel.

RGB in Web Design (CSS Quick Example)
On the web, you can define colors in CSS using rgb() or rgba() (where “a” stands for alpha, or transparency):
cssCopyEdit/* Solid tomato red */
color: rgb(255, 99, 71);
/* Tomato red at 50% transparency */
color: rgba(255, 99, 71, 0.5);
This flexibility lets you layer colors and add visual depth without relying on extra images.
Common Myths About RGB
- “RGB is the same as LED” → Nope. LED is the light technology; RGB is the color system. Not all LEDs can produce RGB colors.
- “RGB on every device is identical” → Different screens have different gamuts and need calibration for color accuracy.
- “RGB works for printing” → It doesn’t—always convert to CMYK for print.
Conclusion
RGB is the language of digital color. Once you understand how red, green, and blue light work together, you can control every pixel, LED, and shade in your projects with confidence.
From choosing the perfect accent color for your website to setting a mood with smart lighting, RGB gives you the freedom to design with light itself.
FAQs
What does RGB stand for?
RGB stands for Red, Green, and Blue—the three primary colors of light. By adjusting the brightness of each color, screens and LEDs can produce millions of different shades.
What is RGB used for?
RGB is used in any device or display that creates color with light. This includes TVs, computer monitors, smartphones, digital cameras, LED lighting, and even gaming accessories like keyboards and headsets.
How is RGB different from CMYK?
RGB is a light-based color model for screens, while CMYK is an ink-based model for printing. RGB starts with black and adds light to create colors, whereas CMYK starts with white paper and subtracts light using colored inks.
Why don’t RGB colors look the same when printed?
Some bright or neon RGB colors can’t be perfectly reproduced with CMYK inks. When printed, these colors may appear duller or slightly different unless the design is converted and adjusted for print.
What’s the difference between RGB and LED?
LED refers to the lighting technology itself. RGB is the color system. An RGB LED can mix red, green, and blue light to create a wide range of colors, while a non-RGB LED may only produce a single color.
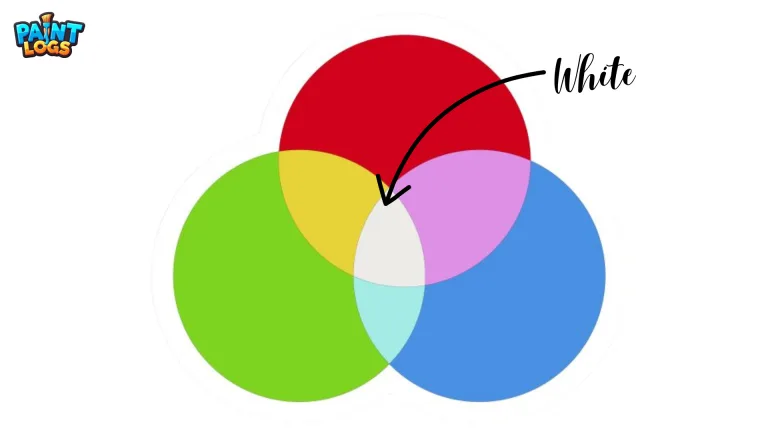
Can RGB make white?
Yes. In the RGB model, when red, green, and blue are all set to their maximum brightness, they combine to produce pure white light.
How do I find the RGB value of a color?
You can find RGB values using a color picker tool in design software like Photoshop, Illustrator, or Figma. There are also free online tools that instantly show you RGB and hex codes for any shade.
What is RGBA?
RGBA is just like RGB but with an extra alpha channel for transparency. This makes it possible to create colors that are partially see-through, which is especially useful in web design and layered graphics.